This activity is part of the FabConnectHer project, dedicated to empowering future female innovators through inspiration, skills and networks to make an impact in the field of STEAM through education, reemployment or entrepeneurship
“Fun Geometry” aims to develop students’ spatial awareness, geometric understanding, creativity, and problem-solving skills by constructing Platonic solids and a geodesic dome using Alquimetricos resources. The lesson emphasizes real-world applications of geometry in art, architecture, and engineering while fostering teamwork and innovation. It is designed for elementary and primary school students aged 8 to 12, combining mathematics, engineering, and art to foster both technical and creative skills.
Understand the properties of Platonic solids:
Develop spatial awareness and geometric understanding:
Apply geometry in real-world contexts:
Enhance problem-solving and teamwork skills:
Foster creativity and exploration:
Instill a Beta & Tech (B&T) mentality:
Encourage reflection and critical thinking:
This activity provides students with a foundational understanding of geometry, its practical uses, and the confidence to innovate, aligning with the inclusive goals of the FabConnectHer project.
Introduce students to the concept of Platonic solids, explaining their history, properties, and applications in real life. Establish the objectives of the activity: to build Platonic solids and a geodesic dome.
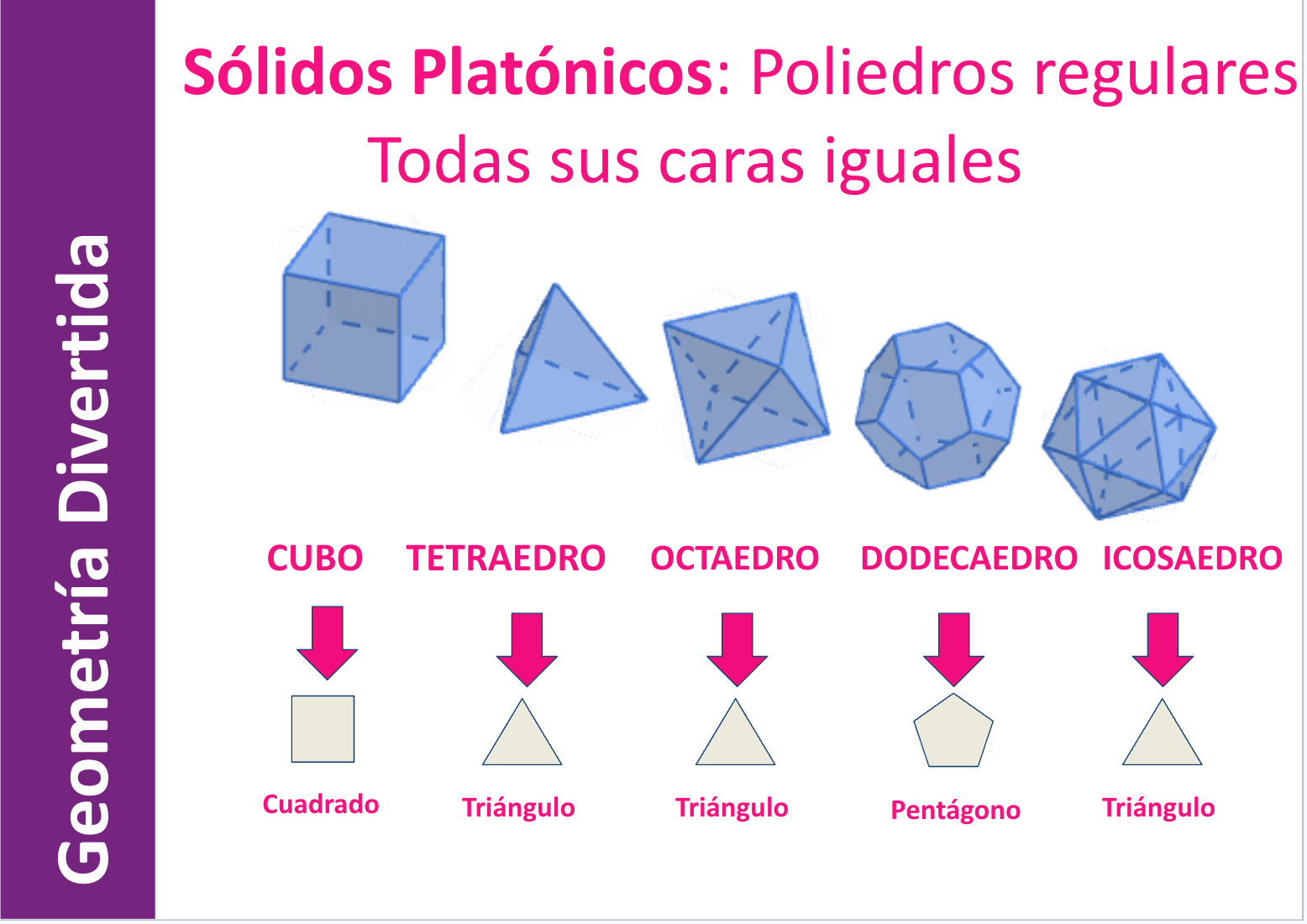


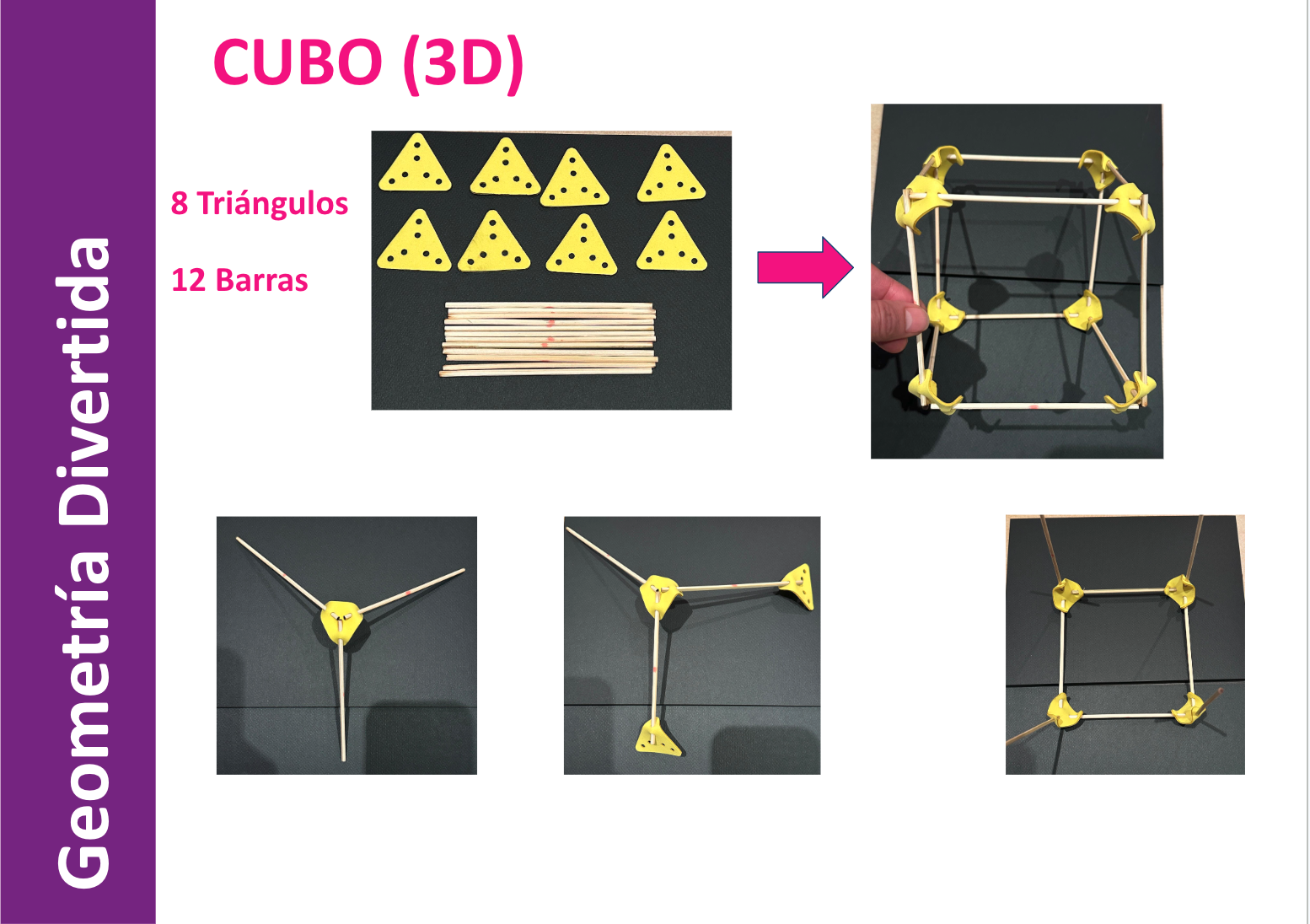
Students learn about and build various Platonic solids, enhancing their understanding of regular polyhedra.

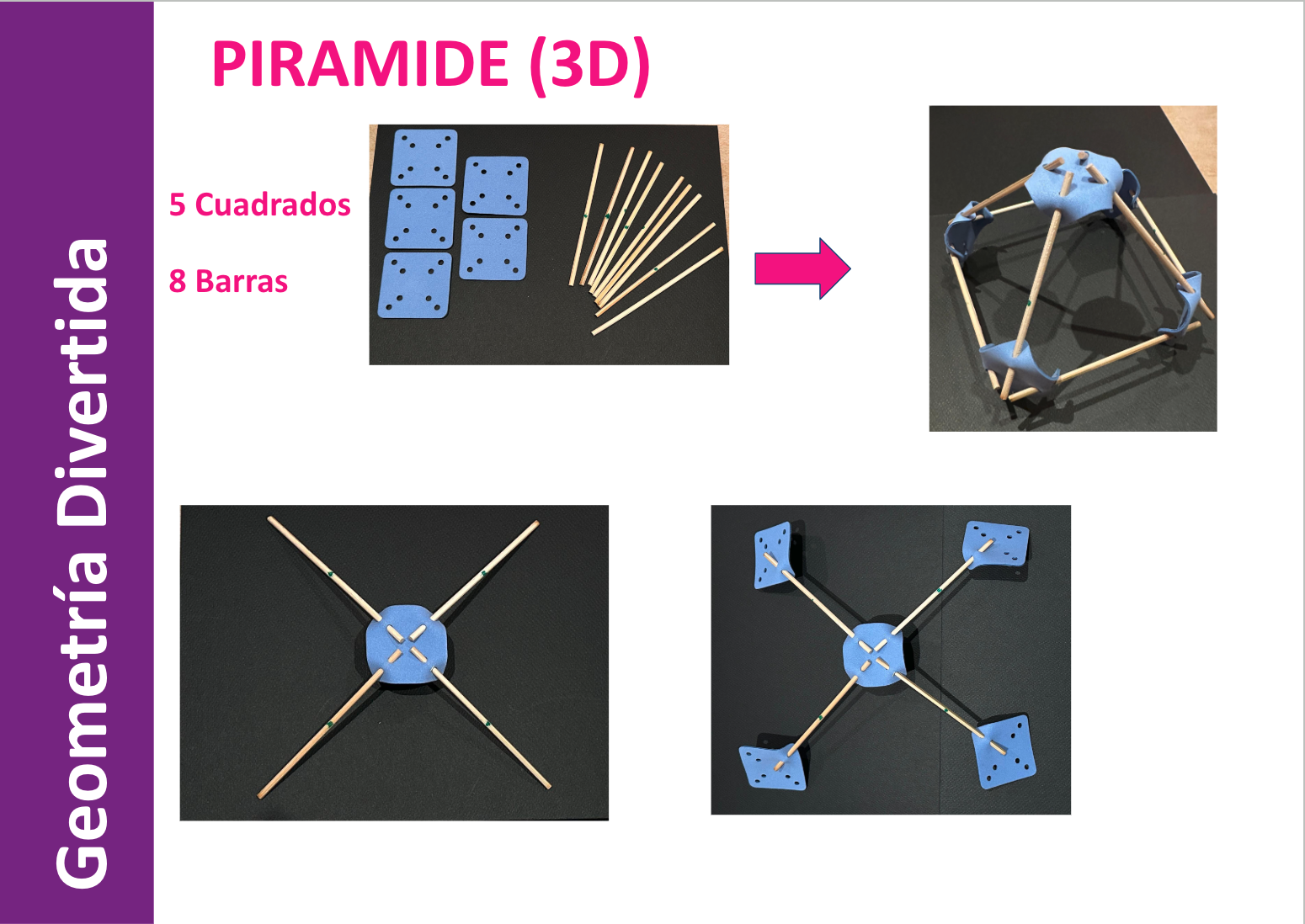
Students apply their knowledge of geometry to construct a geodesic dome, emphasizing teamwork and structural stability.






Students experiment with materials to create their own designs or modify existing ones, fostering creativity and exploration.

Students reflect on the activity, share their learnings, and connect the skills gained to real-life applications.
Having trouble? Let us know by completing the form below. We'll do our best to get your issues resolved quickly.
"*" indicates required fields